Introduction to CNC Machine
In strict adherence to the terminology, there is a difference in the meaning of the abbreviations NC and CNC. The NC stands for the older and original Numerical Control technology, whereby the abbreviation CNC stands for the newer Computerized Numerical Control technology, a modern spin-off of its older relative. However, in practice, CNC is the preferred abbreviation. To clarify the proper, us- age of each term, look at the major differences between the NC and the CNC systems.
Conventionally, an operator decides and adjusts various machines parameters like feed, depth of cut etc. depending on type of job, and controls the slide movements by hand. In a CNC Machine functions and slide movements are controlled by motors using computer programs.
Both systems perform the same tasks, namely manipulation of data for the purpose of machining a part. In both cases, the internal design of the control system contains the logical instructions that process the data. At this point the similarity ends.
A CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machine is a type of automated machine tool that uses computer programming to control the movement and operation of various types of cutting tools. These machines can be used to produce highly precise and complex parts from a wide range of materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
The NC system (as opposed to the CNC system) uses a fixed logical function, those that are built-in and permanently wired within the control unit. These functions can- not be changed by the programmer or the machine opera- tor. Because of the fixed wiring of the control logic, the NC control system is synonymous with the term 'hardwired'. The system can interpret a part program, but it does not al- low any changes to the program, using the control features. All required changes must be made away from the control, typically in an office environment. Also, the NC system re- quires the compulsory use of punched tapes for input of the program information
The modem CNC system, but not the old NC system, uses an internal microprocessor (i.e., a computer). This computer contains memory registers storing a variety of routines that are capable of manipulating logical functions. That means the part programmer, or the machine operator can change the program on the control itself (at the ma- chine), with instantaneous results. This flexibility is the greatest advantage of the CNC systems and probably the key element that contributed to such a wide use of the technology in modern manufacturing. The CNC programs and the logical functions are stored on special computer chips, as software instructions, rather than used by the hardware connections, such as wires, that control the logical functions. In contrast to the NC system, the CNC system is syn- onymous with the term 'software'.
When describing a particular subject that relates to the numerical control technology, it is customary to use either the term NC or CNC. Keep in mind that NC can also mean CNC in everyday talk, but CNC can never refer to the older technology, described in this handbook under the abbreviation of NC. The letter 'C' stands for Computerized, and it is not applicable to the hardwired system. All control systems manufactured today are of the CNC design. Abbreviations such as CNC or CnC are not correct and reflect poorly on anybody that uses them.
Read More about CNC machine:
Types of CNC machine: click here
Different between manual machine and CNC machine: click here
advantages of CNC machine: click here
application of CNC machine: click here
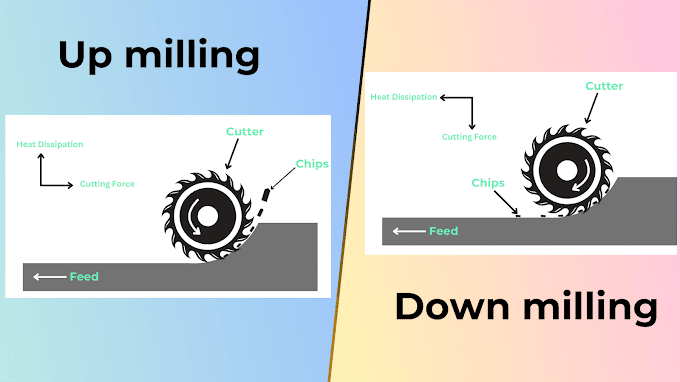
Milling machines: click here
#cncmachine #CNC #vmcmachine #vmv #computernumericalcontrol #verticlemachiningcenter #hmc #hmcmachine #horizontalmachininggcenter
what does cnc stand for in engineering | cnc machine abbreviation | introduction of cnc machine | introduction cnc machine | cnc abbreviation meaning













Thank you.