Milling is material removal process in which cutter rotate against the workpiece at particular RPM and feed incase to remove material from it. generally milling process done in two way, either it's Up milling or Down milling. in up milling cutter and workpiece moves in opposite direction, where in down milling cutter of workpiece moves in same direction to remove material. in this article we see up and down milling definition, process, difference, advantages, disadvantages, applications and quetions regarding up and down milling.
Up and Down milling
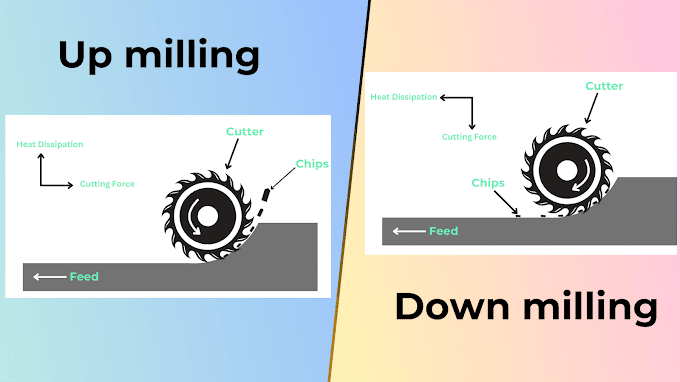
Up Milling
- Up milling which also known as "Conventional Milling" in which the milling cutter rotates in a direction opposite to the feed direction of the workpiece to remove material from workpiece.
- In up milling, the material is removed by the resultant force and this resultant force try to lift the work piece. Due to this reason if we try to machining thin material by this method then due to resultant force thin material are lift.
- During material removal chip thickness very. At the starting chips thickness are minimum and towards the end it's become maximum. Due to this reason Tool wear in case of up milling is High.
- There are some Backlesh in case of up milling, due to which surface finish is poor and tool life is also reduce.
- In case of up milling when chips removes and heat is diffuse towards material hence material properties are changes.
- In case of up milling, coolant pouring on the cutting edge are difficult due to typical nature of cut.
- Burr is form only on unfinished surface due to which its remove in subsequent passes, hence there is not any other process require to remove burr.
Down Milling
- Down milling also known as "Climb Milling" in which, the direction of milling cutter rotation is as same as the workpiece feed direction to remove material.
- In down milling, the resultant force presses the workpiece against the base, due to which requirements of fixtures cost are neglected and also thin material are machined easily.
- The cutter with high rake angle can be used for down milling.
- In down milling chip thickness varying from maximum to minimum. At starting point maximum material are in contact with cutter and towards the end of cutting only point contact of material hence Tool life in case of down milling are high.
- Heat diffusion in case of down milling are towards the direction of chip hence material properties remain same.
- Backlesh in case of down milling are negligible, hence best surface finish and greater tool life are achieve.
- The coolant can be pouring at the cutting zone where cutting is more.
- Burr is formed at the finished surface in opposite side of the relative tool feed, hence these burr are not automatically removed and this leads to degrade cutting quality.
Difference between Up and Down milling
Up Milling vs Down Milling
| Characteristics | Up Milling | Down Milling |
|---|---|---|
| Name | Conventional milling | Climb milling |
| Definition | In up milling, the milling cutter rotates in a direction opposite to the feed direction of the work piece. | In down milling, the direction of milling cutter rotation is the same as the work piece feed direction. |
| Rotation of cutter | Rotation of cutter and feed are opposite. | Rotation of cutter and feed are the same. |
| Force direction | In up milling, the material is removed by the resultant force. | In down milling, the resultant force presses the work piece against the cutter. |
| Chip direction | Chip thrown in upward direction by milling cutter. | Chip thrown in downward direction by milling cutter. |
| Surface finishing | In up milling, poor surface finishing is achieved, making it suitable for roughing operations. | In down milling, a better surface finish is achieved, making it suitable for finishing operations. |
| Backlash | Some backlash. | Backlash free. |
| Chip thickness | In up milling, chip thickness varies from minimum to maximum. | In down milling, chip thickness varies from maximum to minimum. |
| Heat diffuse | In up milling, heat diffuses towards the material, potentially changing work piece properties. | In down milling, heat diffuses towards the chip, keeping work piece properties unchanged. |
| Tool wear | More tool wear. | Less tool wear. |
| Fixture | Due to high load on the work piece, holding devices like fixtures are required in up milling. | In down milling, fixture requirements are minimal. |
| Coolant | Difficulty in pouring the coolant just on the cutting edge due to the nature of the cut. | The coolant can be poured at the cutting zone where cutting force is maximum. |
| Burr | Burr is formed only on the unfinished surface ahead of the relative tool feed; however, the majority of such burrs are removed in subsequent passes. | Burr is formed at the finished surface on the opposite side of the relative tool feed, and these burrs are not removed automatically, degrading cutting quality. |
| Cost | In up milling, overall cost is comparatively high due to high tool wear and fixture requirements. | In down milling, overall cost is lower. |
| Material | For brittle materials like ceramics, up milling is useful. | In the case of brittle materials, down milling is not a viable process. |
Advantages of up milling
- In case of up milling due to typical nature of cut pouring of coolant is only at the cutting edge hence coolant requirements are less.
- Burr is form only on unfinished surface which removed in subsequent passes hence there is not extra process require to remove burr.
- High surface integrity, because during the tooth engagement its rub the surface and suface finishing are also good.
- The fatigue limit of up milled surface are higher.
- Best suitable for Brittle material like ceramic.
Disadvantages of up milling
- There is some of Backlesh error in case of up milling.
- Poor suface finishing.
- Work piece properties are changes due to heat diffuse towards material.
- Tool wear is high.
- Force try to lift the workpiece hands fixture must required in up milling.
- Cost incase of up milling are high.
Advantages of down milling
- Down milling are backlesh free.
- Best surface finishing are archive.
- Heat diffuse towards the chip direction hence work piece properties remain same.
- Tool wear is less.
- Due to force act opposite to the base there is not extra fixture requirements in case of down milling.
- Cost incase of down milling is less.
Disadvantages of down milling
- Coolant can be poured at the cutting zone where cutting force are more hence high coolant required.
- Burr is form towards finished parts, hence after the process we have to remove it manually or by the grinders.
- In case of down milling operation induce poor surface integrity characterized which results in damage defects like (metal folds and micro cracks).
- The fatigue limit in down milled surface are lower.
- Not suitable for Brittle material.




%20(1).png)





Thank you.