Golden rule of Milling
Thick in Thin out
- Before doing milling operation remember the golden rule of machine, according to this during the time of milling operation cutter has to cut thick at start and towards end of operation this thickness is low. If we do milling operation as per this rule than we able perform stable milling process.
(toc)Table of content
UP Milling
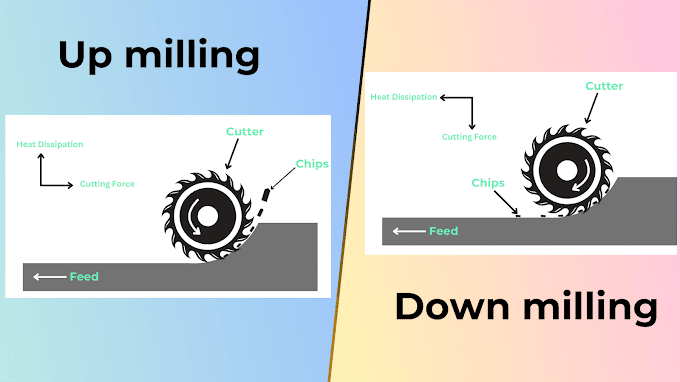
- Up milling which also known as Conventional milling is the materials removing process from metal and non metal where rotating cutter removed the material. In case of Up milling direction of rotation of milling cutter and workpiece feed direction is opposite in order to remove material.
- In this case chip thickness at engagement of tooth is low and at the end due to high engagement of tool with material chip thickness is high and due to this reason cutting force or load is gradually increase incase of up milling.
- One of the major Disadvantage of UP milling is tendency to lift the workpiece, due to this heavy fixture required and also poor surface finishing obtained in this process.
Down milling
- Down milling which also known as Climb milling in which cutter rotates in same direction to direction of feed of workpiece in order to remove material.
- In Down milling chip thickness is maximum at engagement of tooth and towards the end it's minimum. In Down milling impact load act on workpiece, due to which there is not requirements of heavy fixtures, also better surface finishing achieve in Down milling.
Diffrence between Up and Down milling
1. Chip load
- Chip load on teeth of tool in case of UP milling increases gradually from zero at the point of engagement to maximum at the point of disengagement of tool, due to this heat generate in process is diffuse in surface of workpiece.
- Where in case of DOWN milling Chip load on teeth of tool is maximum at the point of engagement to zero at point of disengagement (decrease gradually), but generated heat is transfer with chip.
2. Load type
- In case of UP milling chips engagement is minimum to maximum hence load also act in same sequence of low to high, hence gradual load act on workpiece.
- On other hand load in DOWN milling is impact type load. Because in start engagement of tool teeth with chip material almost two times of size of chips at end of operation, due to which overall chip thickness is bigger in Down milling. Due to acting impact load on workpiece milling machine structure is rigid required in Down milling.
- With horizontal axis milling machine, cutting force in up milling mode is directed upward, and thus it tends to lift off the workpiece from the worktable. Accordingly, rigid and expensive fixture is required for firmly mounting the workpiece.
- In down milling mode, the cutting force is directed downward, and thus it tends to press the workpiece rather than lift off. So cheaper fixture can be
3. Cutting force
- Cutting force is important characteristics incase of milling process to achieve good surface finishing, minimal load required and many more. As you can see in above image that cutting force in case of UP milling is act in upward direction hence force try to lift workpiece, because of this reason heavy fixtures with multiple champing required incase of UP milling.
( F_{c})^{2} \ =\ F_{c} cos\ +F_{c} sin
- Direction of Cutting force in Down milling is in Downward direction which tends to push the workpiece hence fixture required is minimal.
4. Heat generation
- In the Up milling due to gradual increase of load, heat generation at the end is high and this chip with high heat have the tendency to weld with teeth of tool due to which tool wear increase.
- Where on other side in down milling heat generation is less compared to Up milling, but this chips are re deposit on the surface of machined workpiece, because of this surface finishing is degrade incase of down milling.
5. Tool wear
- Up milling, in which tool come in contact with minimum to maximum chip thickness, because of this due to rubbing at beginning work hardening is occur and also due to lower temperature around cutting edge of workpiece.
- Apart from this in Down milling operation maximum chips came in contact at starting and towards end its minimum and also chip thickness is two times bigger than Up milling, this chips will reduce tool wear and produce better surface finish because of high cutting force.
6. Defect
- Notch wear in down milling
7. Chip surface temperature
- Chip surface temperature is not depend on process of milling either it's Up or down milling, but depend on tool wear. But experimental results prove that chip surface temperature in down milling is higher than up milling.
8. Burr
- Average thickness of burred formed in Down milling is higher than up milling In UP milling burr is formed and thrown upward hence is collect on unfinished surface and this burr is removed in subsequent passes.
- But in Down milling burr formed in unfinished surface. This burr is not automatically removed and this leads to degrade cutting quality. So in this case we have to perform operation to remove burr for better surface finish.
9. Workpiece thickness
- In Up milling, cutting force is try to lift the workpiece hence we can't easily machined thin material in UP milling.
- Where in down milling cutting force try to compress the workpiece, hence we can easily machining thin components by down milling.
- Thin work piece samples, if machined using up milling mode, may get distorted due to upward cutting force, Chances of distortion of thin work piece samples are less with down milling mode if proper support in bottom is provided.
10. Fatigue limit & Surface integrity
- From many experiments which prove that Surface to be produce in UP milling is subjected to compressive residual strees due to high work hardening. Fatigue limit of UP milling is higher compared to down milling to better surface integrity.
- Down milling operations induces power surface integrity and it's slightly affected by residual tensile stress hence fatigue limit of down milling is lower 20 to 30% compared to UP milling.
- The fatigue limit of this up-milled surface is higher This machined surface is highly work-hardened and subjected to compressive residual stresses.
- The fatigue limit of this down-milled surface is lower. This machined surface is slightly work-hardened and subjected to minute compressive residual stresses.
Conclusion
- Experiment show that employed of combination of up and down milling in path strategy can reduce cycle time with better productivity and surface finish..
What is the difference between up and down milling?
- Up milling which also known as Conventional milling is the materials removing process from metal and non metal where rotating cutter removed the material. In case of Up milling direction of rotation of milling cutter and workpiece feed direction is opposite in order to remove material.
- Down milling which also known as Climb milling in which cutter rotates in same direction to direction of feed of workpiece in order to remove material.
Which milling gives better surface finish?
- In the down milling, Surface finishing is achieved slightly better than UP Milling because chip thickness is maximum at engagement of tooth and towards the end it's minimum. In Down milling impact load act on workpiece, due to which there is not requirements of heavy fixtures, also better surface finishing achieve in Down milling.
What are the advantages of down milling?
- Down milling are backlesh free.
- Best surface finishing are archive.
- Heat diffuse towards the chip direction hence work piece properties remain same.
- Read more.
What is the golden rule of milling?
- "Thick in Thin out" remember this golden rule of milling that, tool in maximum engage with workpiece at starting and at ending minimum tool will engage with material for achived better milling operation.
What is the advantage of up milling?
- In case of up milling due to typical nature of cut pouring of coolant is only at the cutting edge hence coolant requirements are less.
- Burr is form only on unfinished surface which removed in subsequent passes hence there is not extra process require to remove burr.
- Read more.









Thank you.